| Rank | Program Name | Location | Overall Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stanford University Graduate School of Business | Stanford, California, United States | 100.0 |
| 2 | Harvard Business School | Boston, Massachusetts, United States | 99.5 |
| 3 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management | Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States | 99.1 |
| 4 | University of Pennsylvania Wharton School | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States | 98.9 |
| 5 | University of Chicago Booth School of Business | Chicago, Illinois, United States | 98.7 |
| 6 | London Business School | London, United Kingdom | 98.5 |
| 7 | INSEAD | Fontainebleau, France and Singapore | 98.3 |
| 8 | Yale School of Management | New Haven, Connecticut, United States | 98.1 |
| 9 | Columbia Business School | New York City, New York, United States | 98.0 |
| 10 | University of California, Berkeley Haas School of Business | Berkeley, California, United States | 97.9 |
Factors Influencing QS Ranking
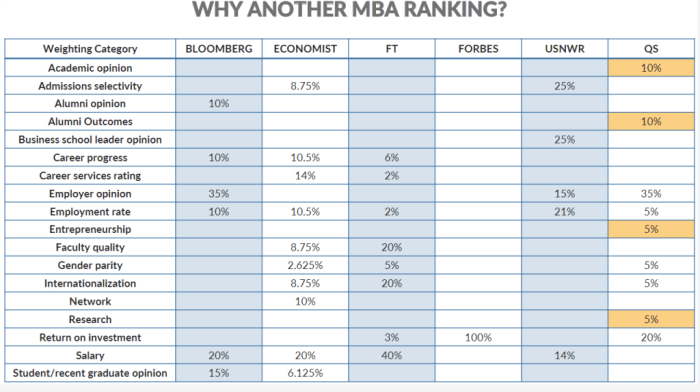
The QS Ranking for MBA programs is a comprehensive evaluation that considers various factors to determine the overall standing of each program. These factors play a crucial role in shaping the ranking and can significantly impact the position of a particular program.
The key factors that influence the QS Ranking include:
Academic Reputation
- This factor measures the reputation of a program among academics and professionals in the field.
- It is based on surveys conducted with academic experts and recruiters, who assess the program’s quality, research output, and teaching excellence.
Employer Reputation
- This factor reflects the reputation of a program among employers.
li>It is based on surveys conducted with employers who hire MBA graduates, and it measures the program’s ability to prepare students for the job market.
Faculty-to-Student Ratio
- This factor measures the ratio of faculty members to students in a program.
- A lower ratio indicates that students have more access to faculty members and can benefit from personalized attention.
Class Size, Mba qs ranking
- This factor measures the average class size in a program.
- Smaller class sizes can foster more interactive learning experiences and allow for closer interaction between students and faculty.
Research Citations per Faculty
- This factor measures the average number of research citations per faculty member in a program.
- It reflects the program’s research output and the impact of its research on the field.
International Faculty Ratio
- This factor measures the percentage of faculty members in a program who are from outside the country where the program is located.
- A higher international faculty ratio indicates a program’s global reach and diversity.
International Student Ratio
- This factor measures the percentage of students in a program who are from outside the country where the program is located.
- A higher international student ratio indicates a program’s ability to attract students from around the world.
Career Services
- This factor measures the quality of career services provided by a program.
- It includes factors such as career counseling, job placement assistance, and alumni networking opportunities.
Salary
- This factor measures the average salary of graduates from a program.
- It reflects the program’s ability to prepare students for high-paying jobs.
Comparison of QS Ranking with Other Rankings

The QS Ranking is one of the most widely recognized MBA rankings, but it is not the only one. Other notable rankings include the Financial Times Ranking and the U.S. News & World Report Ranking.