- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Creates detailed images of the brain’s structure and function.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Provides cross-sectional images of the brain, useful for detecting structural abnormalities.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Measures brain activity by tracking the uptake of radioactive tracers.
- Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT): Similar to PET, but uses different tracers.
Age-Related Brain Changes, Aging brain news
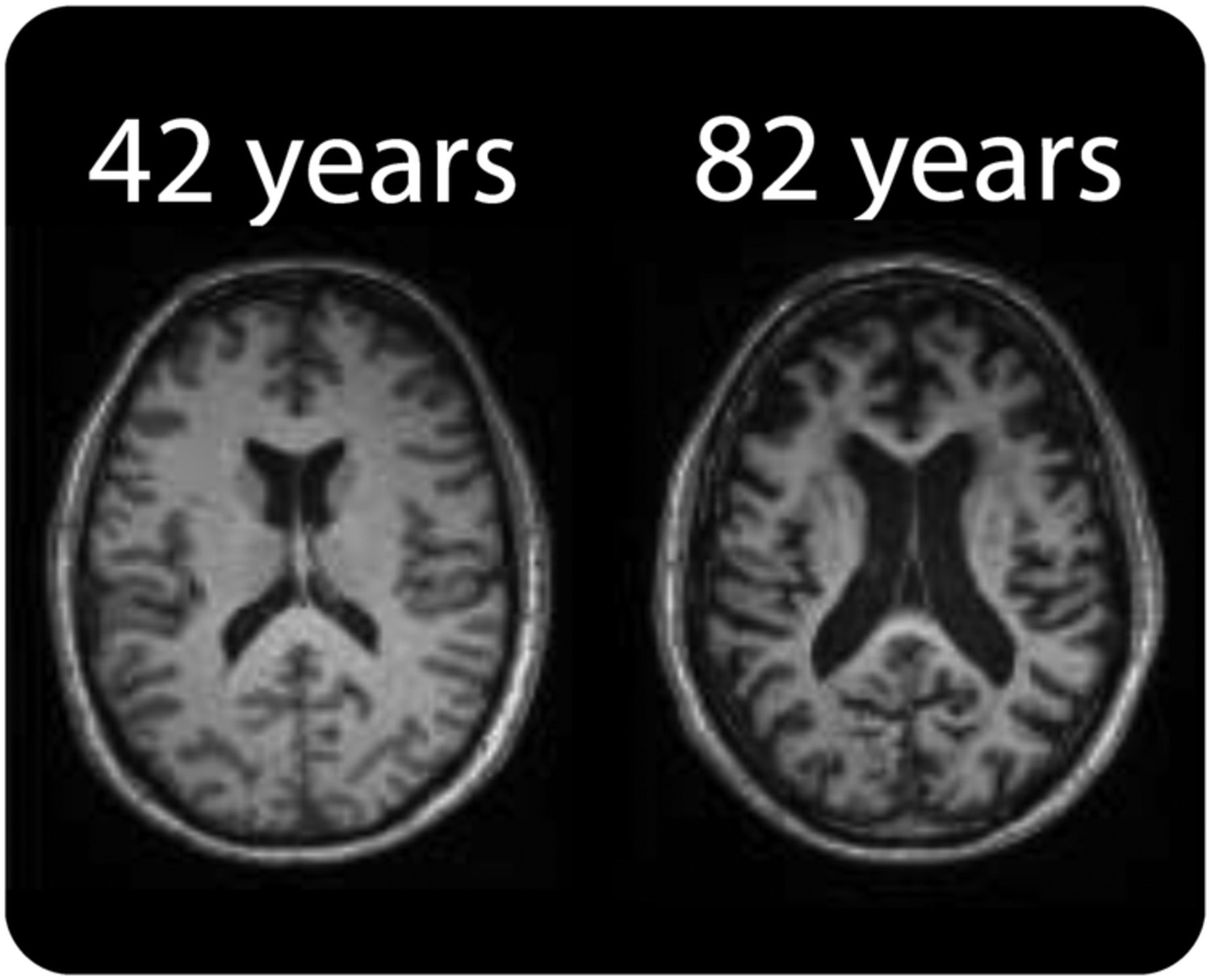
Brain imaging studies have revealed several age-related brain changes, including:
- Cortical thinning: The cerebral cortex, responsible for higher-order functions, becomes thinner with age.
- Ventricular enlargement: The ventricles, fluid-filled cavities within the brain, enlarge with age.
- White matter hyperintensities: Bright spots on MRI scans, indicating damage to white matter, become more common with age.
Neurological Disorders and Aging
Brain imaging is also valuable in diagnosing and studying neurological disorders associated with aging, such as:
- Alzheimer’s disease: PET and MRI scans can detect changes in brain activity and structure associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Parkinson’s disease: SPECT and MRI scans can help visualize the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain.
- Stroke: CT and MRI scans can detect brain damage caused by a stroke.
Innovative Therapies for Aging Brains

The aging brain presents unique challenges, and researchers are constantly exploring innovative therapies to address cognitive decline and neurological disorders in older adults. These therapies aim to improve brain function, preserve cognitive abilities, and enhance overall brain health.