Alzheimer’s Disease
- Symptoms: Memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, difficulty with language, and changes in personality.
- Diagnosis: Medical history, physical and neurological exams, cognitive tests, and brain scans.
- Treatment: Medications to manage symptoms, cognitive stimulation therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Parkinson’s Disease
- Symptoms: Tremors, rigidity, slow movement, impaired balance, and difficulty with speech.
- Diagnosis: Medical history, physical and neurological exams, and brain scans.
- Treatment: Medications to improve movement, physical therapy, and speech therapy.
Stroke
- Symptoms: Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, and loss of balance.
- Diagnosis: Medical history, physical and neurological exams, brain scans, and blood tests.
- Treatment: Emergency medical care, medications to prevent blood clots, rehabilitation therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Neurological disorders can significantly impact cognitive function and quality of life. They can lead to memory loss, impaired judgment, difficulty with movement, and social isolation. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage symptoms and improve outcomes.
Cognitive Changes with Aging
As we age, it is normal to experience some changes in our cognitive abilities. These changes can include declines in memory, attention, and processing speed. However, it is important to note that not all age-related cognitive changes are a sign of dementia. Typical age-related cognitive decline is a gradual process that does not interfere with everyday activities. Dementia, on the other hand, is a more severe condition that can cause significant impairment in cognitive function and interfere with daily life.
Coping with Cognitive Changes
There are a number of things that we can do to cope with cognitive changes and maintain our independence as we age. These include:
- Staying active both physically and mentally.
- Eating a healthy diet.
- Getting enough sleep.
- Managing stress.
- Staying socially connected.
- Using assistive devices, such as magnifiers or hearing aids, if needed.
By following these tips, we can help to slow the progression of cognitive decline and maintain our independence for as long as possible.
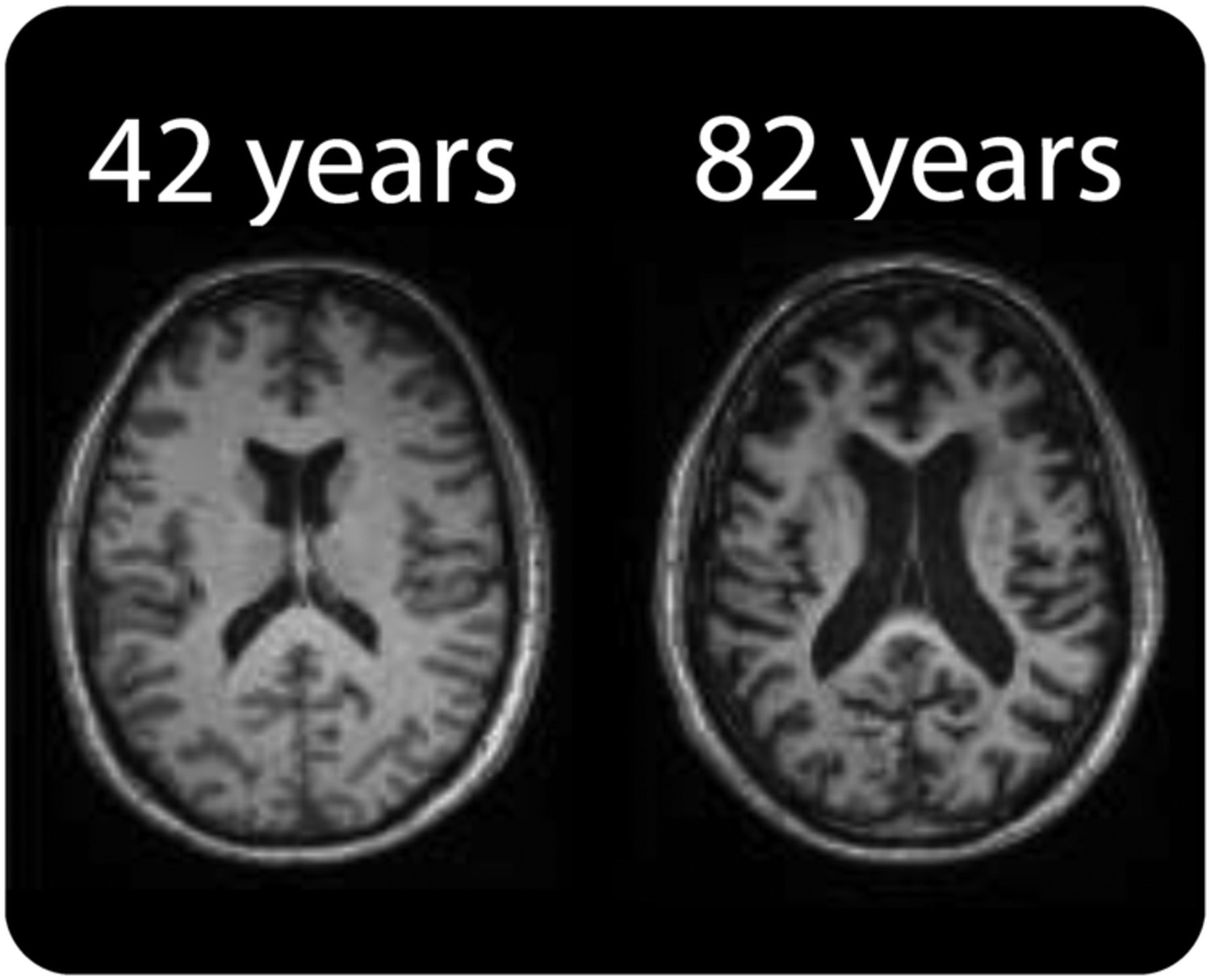
Brain Imaging and Aging
Brain imaging techniques play a crucial role in studying brain aging. They allow researchers to visualize the brain’s structure and function, providing insights into age-related changes and neurological disorders.
Different types of brain imaging methods include: