Welcome to the world of masters programs with biology degree, where scientific curiosity meets professional excellence. Whether you’re a recent graduate or a seasoned professional seeking career advancement, this guide will help you navigate the diverse landscape of master’s programs in biology and empower you to make informed decisions about your future.
Dive into the fascinating realm of biology and explore the myriad specializations that await you, from molecular biology to ecology and conservation. Discover the career paths that lie ahead, from research and development to teaching and environmental management. Get ready to embark on a journey that will transform your understanding of life sciences and propel your career to new heights.
Master’s Programs with a Biology Degree: Masters Programs With Biology Degree

Types of Master’s Programs, Masters programs with biology degree
Master’s programs with a biology degree offer specialized training in various subfields of biology, such as:
- Molecular biology
- Cell biology
- Ecology
- Evolutionary biology
- Neuroscience
Duration, Cost, and Admission Requirements
The duration of a master’s program in biology typically ranges from 1.5 to 2 years, depending on the program and the student’s pace of study. Costs vary widely depending on the institution and program, but generally range from $30,000 to $80,000. Admission requirements typically include a bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field, a minimum GPA, and GRE scores.
Career Opportunities
Graduates of master’s programs in biology have a wide range of career opportunities in academia, industry, and government. They can work as researchers, professors, lab technicians, environmental scientists, or science writers.
Types of Master’s Programs in Biology

Master’s programs in biology offer a wide range of specializations, each tailored to a specific area of biological research. These programs provide advanced training in cutting-edge research techniques, theoretical frameworks, and practical applications.
Specializations within Biology
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: Focuses on the structure, function, and interactions of biological molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Research opportunities include studying gene expression, protein synthesis, and metabolic pathways.
– Example universities: Harvard University, Stanford University, University of California, Berkeley
Cell and Developmental Biology: Explores the structure, function, and development of cells and tissues. Research opportunities include investigating cell signaling, cell division, and tissue regeneration.
– Example universities: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Cambridge, University of California, San Francisco
Ecology and Evolutionary Biology: Studies the interactions between organisms and their environment, as well as the evolution of species. Research opportunities include studying population dynamics, ecosystem ecology, and evolutionary processes.
– Example universities: Yale University, Princeton University, University of Oxford
Genetics: Focuses on the inheritance and variation of genetic material. Research opportunities include studying gene mapping, genome sequencing, and genetic engineering.
– Example universities: University of Washington, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Johns Hopkins University
Immunology: Explores the immune system and its role in defending against pathogens. Research opportunities include studying immune cell function, antibody production, and vaccine development.
– Example universities: University of Pennsylvania, University of Toronto, University of California, Los Angeles
Microbiology: Studies microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Research opportunities include investigating microbial ecology, infectious diseases, and antibiotic resistance.
– Example universities: University of California, San Diego, University of Michigan, Cornell University
Neuroscience: Explores the structure and function of the nervous system. Research opportunities include studying brain development, neural circuits, and neurological disorders.
– Example universities: University of California, San Francisco, Columbia University, University College London
Physiology: Studies the function of organs and organ systems in living organisms. Research opportunities include investigating cardiovascular function, respiratory physiology, and endocrine regulation.
– Example universities: University of Oxford, University of Cambridge, Harvard University
Plant Biology: Focuses on the biology of plants, including their structure, function, and evolution. Research opportunities include studying plant genetics, photosynthesis, and plant-environment interactions.
– Example universities: University of California, Davis, Cornell University, University of Edinburgh
Choosing the Right Master’s Program

Selecting the right master’s program is crucial for your career advancement. To make an informed decision, assess your interests and career goals. Consider the program’s reputation, faculty expertise, and research facilities. Attend virtual or in-person events, connect with current students, and explore program websites to gather insights.
Factors to Consider
* Program Reputation: Look for programs with a strong reputation in your field of interest. Check rankings, research output, and industry connections.
* Faculty Expertise: Consider the faculty’s research interests and publications. Ensure they align with your research goals and can provide valuable guidance.
* Research Facilities: Access to state-of-the-art research facilities is essential for hands-on experience and research opportunities. Inquire about the availability of equipment, labs, and research grants.
Finding and Applying to Master’s Programs
* Search Online: Utilize search engines, university websites, and databases to find potential programs.
* Attend Virtual/In-Person Events: Participate in webinars, open houses, and conferences to connect with program representatives and learn more about their offerings.
* Connect with Current Students: Reach out to current students through social media or email to gain insights into the program’s culture, coursework, and research opportunities.
* Explore Program Websites: Thoroughly review program websites for information on curriculum, faculty, research facilities, and admission requirements.
* Prepare a Strong Application: Submit a well-written personal statement, transcripts, letters of recommendation, and any required research proposals.
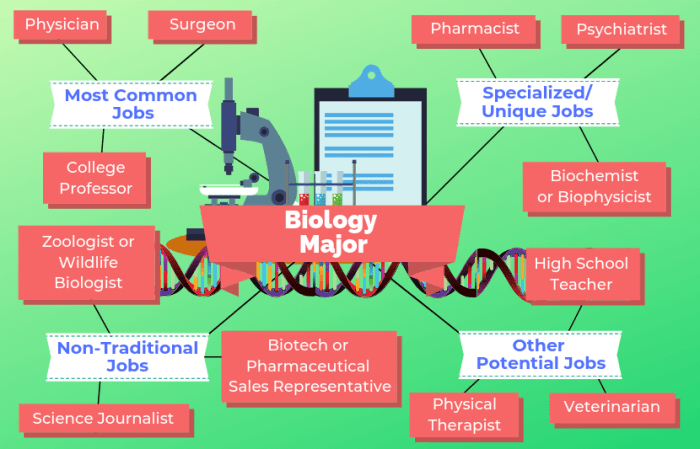
Career Paths for Graduates with a Master’s in Biology
Graduates with a Master’s in Biology have a wide range of career opportunities in various fields. The advanced knowledge and skills acquired through their studies equip them for diverse roles, including research, teaching, industry, and healthcare.
Let’s delve into some of the prominent career paths available to graduates with a Master’s in Biology: